Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University
RNDr. Miroslava Beňovská, Ph.D., Mgr. Ondřej Wiewiorka, MUDr. Jana Tůmová
Crystals
The presence of crystals and amorphous microcrystalline deposits in urine is not considered a significant clinical finding. However, both parameters are determined and their amount is evaluated.
Crystals have various crystalline structure and they occur in many forms. The pH of urine is important factor for their formation and structure, although it is sometimes difficult to distinguish them even then. In that case, the elements could be classified only as crystals – without further specification.
The most frequent crystals in urine are: oxalate and uric acid (in acidic urine) or phosphate (in alkaline urine). Rarely found crystals in urine: bilirubin, cysteine, leucine, tyrosine or drug. We distinguish two types of amorphous microcrystals – amorphous urates in acidic urine and amorphous phosphates in alkaline urine.
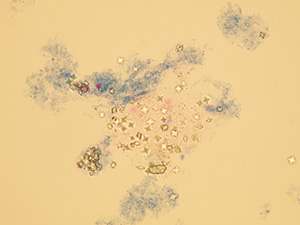
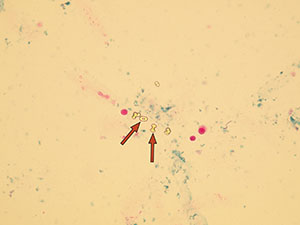
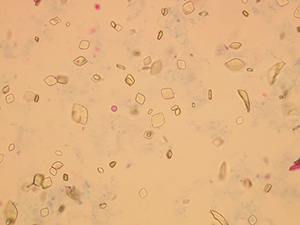
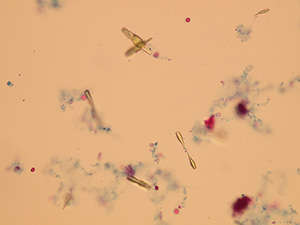
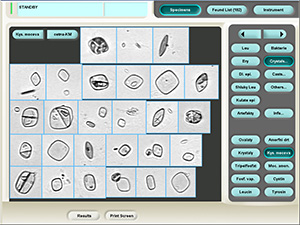
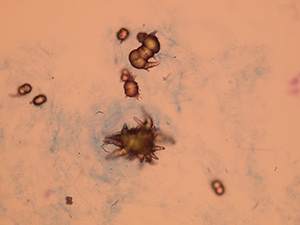
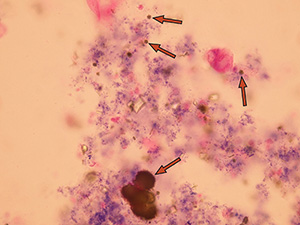
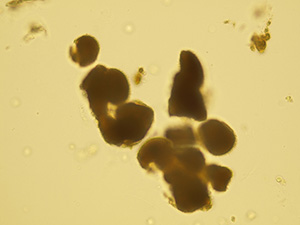
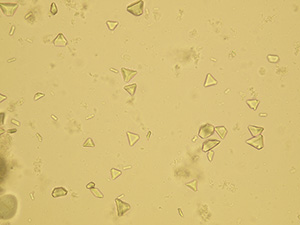
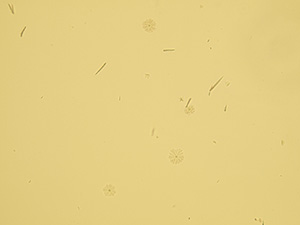
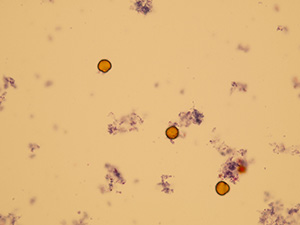
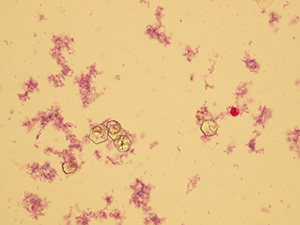
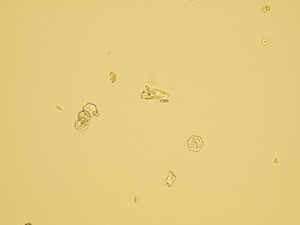
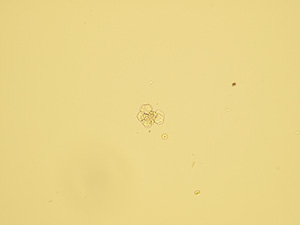
Oxalates
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
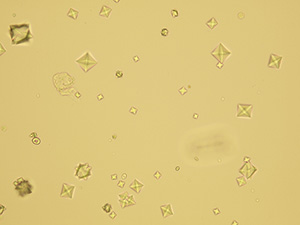
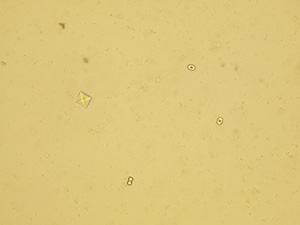
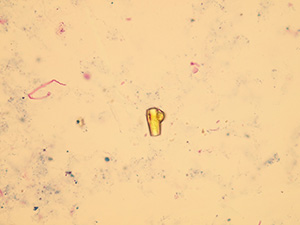
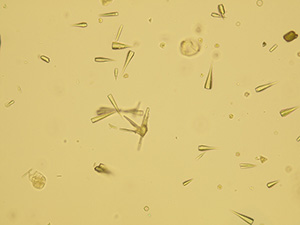
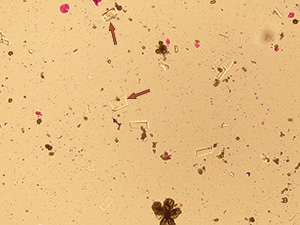
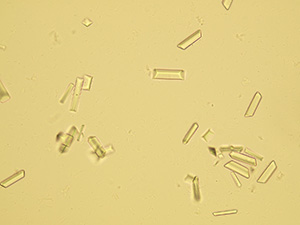
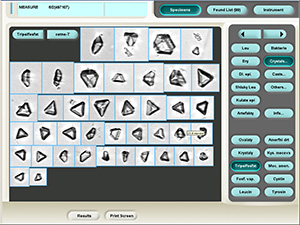
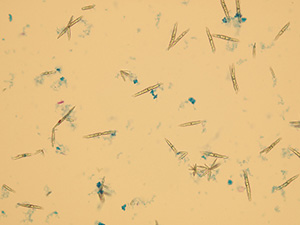
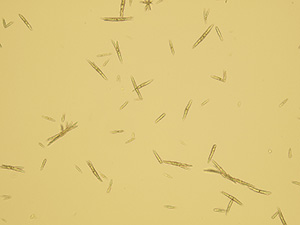
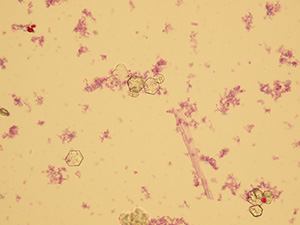
Uric acid
Various forms of crystals of uric acid
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
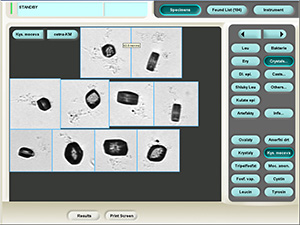
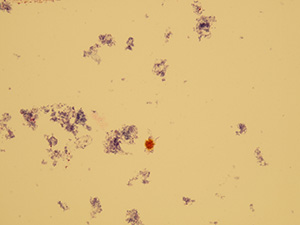
Ammonium urate
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
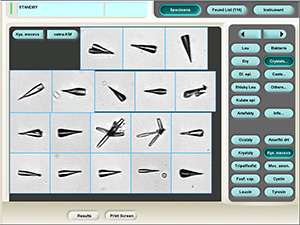
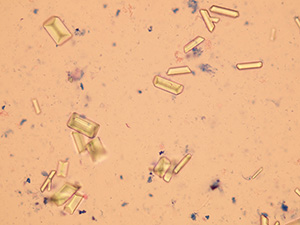
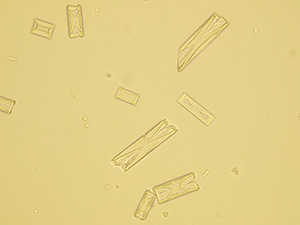
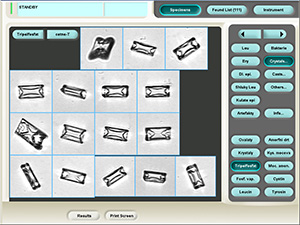
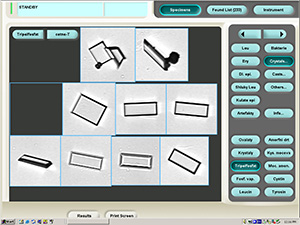
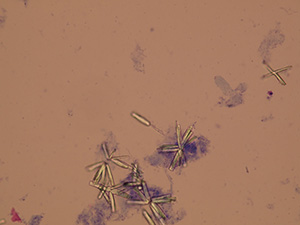
Triple phosphate
Ammonium magnesium phosphate crystals (Triple phosphate).
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
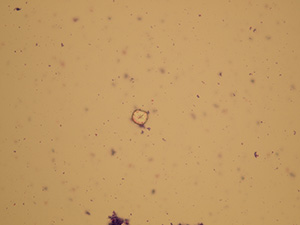
Calcium phosphate
These crystals can be differentiated from uric acid crystals by polarization microscopy. Unlike uric acid, calcium phosphate doesn't turn polarized light.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
Bilirubin
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
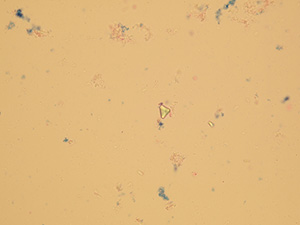
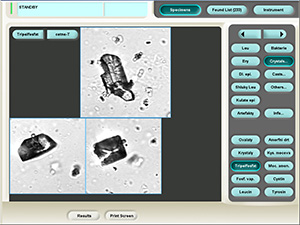
Cystine
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
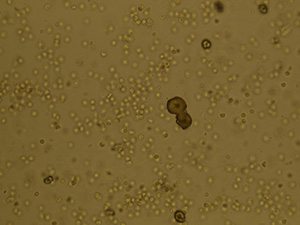
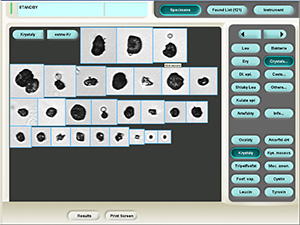
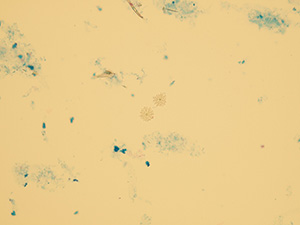
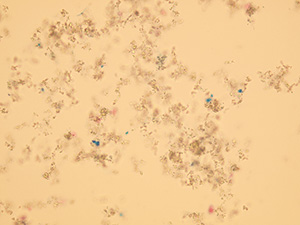
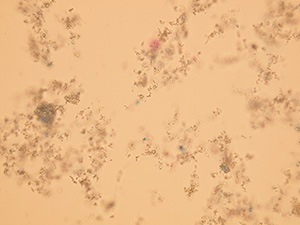
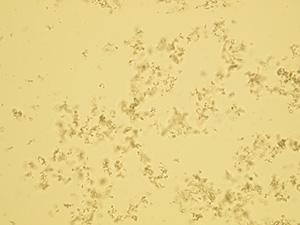
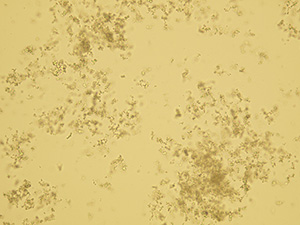
Amorphous microcrystals
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from iQ 200 analyzer (IRIS)
Mgr. Ondřej Wiewiorka , MUDr. Jana Tůmová|
KLT, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University |
Back to Homepage, accessibility |
| Service Center for E-learning
| Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University, 2015
Centrum interaktivních a multimediálních studijních opor pro inovaci výuky a efektivní učení | CZ.1.07/2.2.00/28.0041