Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University
RNDr. Miroslava Beňovská, Ph.D., Mgr. Ondřej Wiewiorka, MUDr. Jana Tůmová
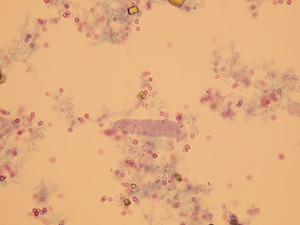
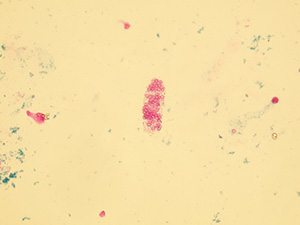
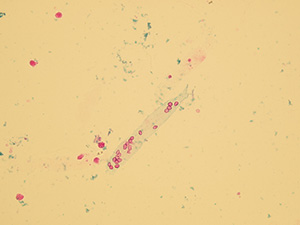
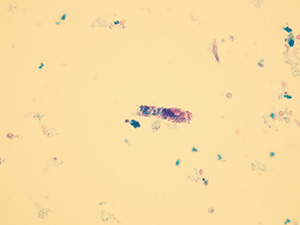
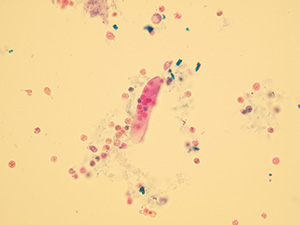
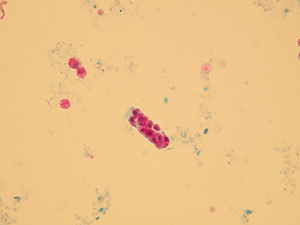
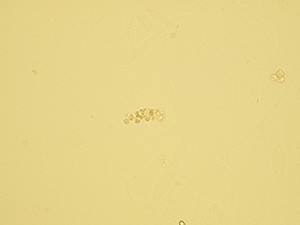
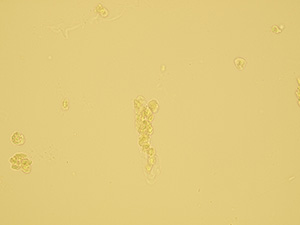
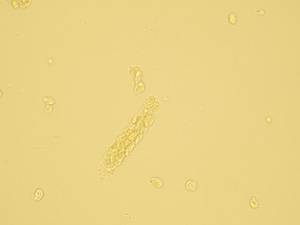
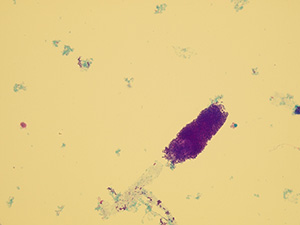
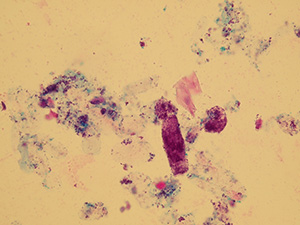
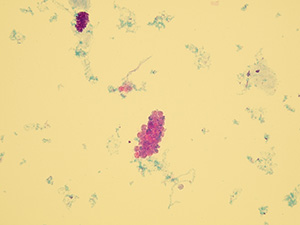
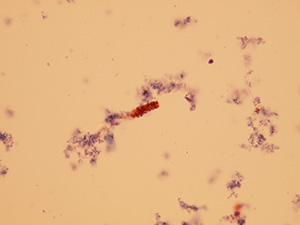
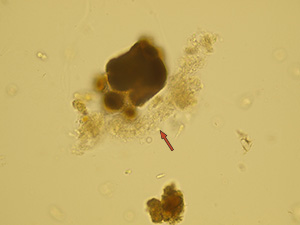
Casts
These elements are formed in the kidney tubules by Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein precipitation. The mucoprotein is secreted from renal tubule cells. Their formation is reinforced by acidic pH in urine, higher concentration of plasmatic proteins, dehydration and excessive physical activity. Their shape copies the shape of a tubule with defined outer line, parallel sides and round ends.
We distinguish hyaline, cellular, granular, wax, lipid, bacterial and combined casts. The cast is classified as cellular or granular cast only if the amount of material inside takes up to 1/3 of its volume. Otherwise, it is called hyaline cast. The cast goes through different stages of development with increasing time in the kidney tubule: cell cast → granular cast → waxy cast.
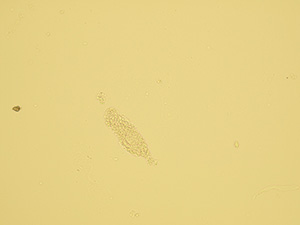
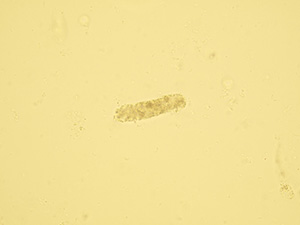
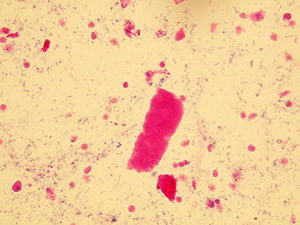
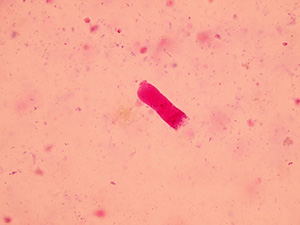
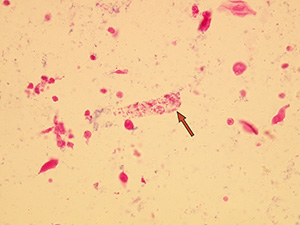
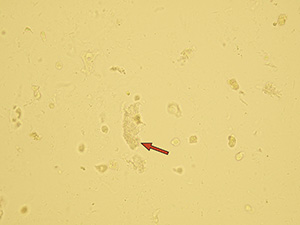
Hyaline casts
Hyaline casts are formed only by Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein without any other elements or their fragments inside. Due to their composition, they are almost undetectable in native sediment.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from FUS-2000 analyzer (DIRUI)
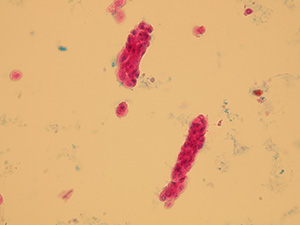
Cell casts
Cellular casts comprise of cells that may occur in renal tubules (leukocytes, erythrocytes and tubular epithelia) entrapped in Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein matrix. We recognize leukocyte casts, erythrocyte casts and renal tubular epithelial cell casts. In some cases, the cells in the cast cannot be accurately determined and the cast is therefore categorized as cellular.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from FUS-2000 analyzer (DIRUI)
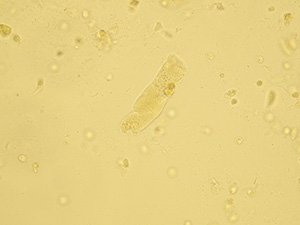
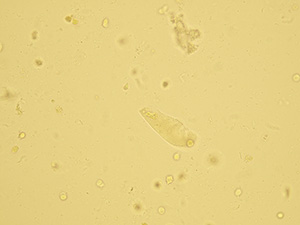
Granular casts
Granules inside these casts are formed after decomposition of cells in the cast or a tubule. Granular casts may vary from coarsely granular including cell particles to finely granular that are turning to waxy casts. Small number of these casts may occur after intensive physical activities (patients who were exposed to cold conditions or cold hardening). Increased concentration of granular casts is strongly pathological.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from FUS-2000 analyzer (DIRUI)
Waxy casts
Waxy casts are the clinically most serious type of casts and they are also called the casts of renal failure. They occur in patients with chronic kidney diseases. Their structure is homogenous, they have the biggest size and their endings are often broken. Sometimes they are partially made of granular matter. They indicate tubule damage.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from FUS-2000 analyzer (DIRUI)
Fatty casts
Fatty casts in protein matrix contain fat inclusions. They are related to strong insufficiency, nephritic syndrome, diabetics and mercury intoxication.
Stained sediment
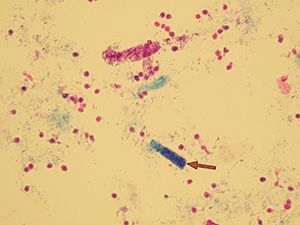
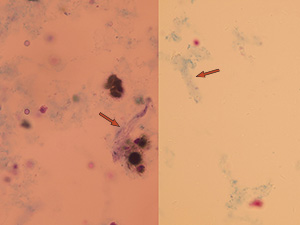
Bacterial casts
Bacterial casts are composed of bacteria in a protein matrix. They may be found in acute pyelonephritis or intrinsic renal infection. Bacterial casts should be seen in association with loose bacteria, leukocytes, and leukocyte casts. Their occurrence is extremely rare, due to their fragility and also commonly used antibiotic treatment.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from FUS-2000 analyzer (DIRUI)
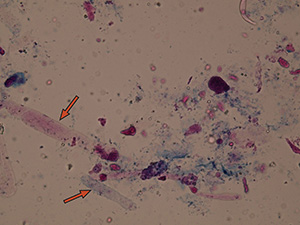
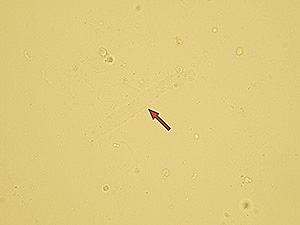
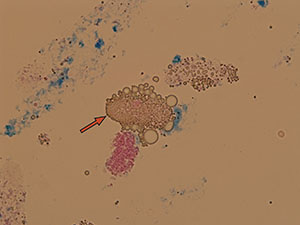
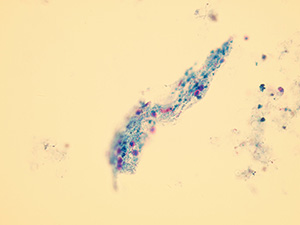
Pseudocasts
Pseudocasts are structures of aggregates that resemble and may be mistaken for casts because of their shape. They are without diagnostic significance. Such structures include mucus threads, leukocytes entrapped in mucus, rolled squamous epithelial cells, aggregates of amorphous urates, calcium oxalate crystals and so on. Artifacts don’t belong in this category.
Stained sediment
Native sediment
Pictures from FUS-2000 analyzer (DIRUI)
Mgr. Ondřej Wiewiorka, MUDr. Jana Tůmová|
KLT, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University |
Back to Homepage, accessibility |
| Service Center for E-learning
| Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University, 2016