The third step when evaluating a journal is to try learning about the way the journal operates. In the case of journals with open peer review, it is necessary to read some peer reviews and the communication between the reviewers and the editor, as this provides the most accurate information about the review process and the editor’s reasons for accepting an article.
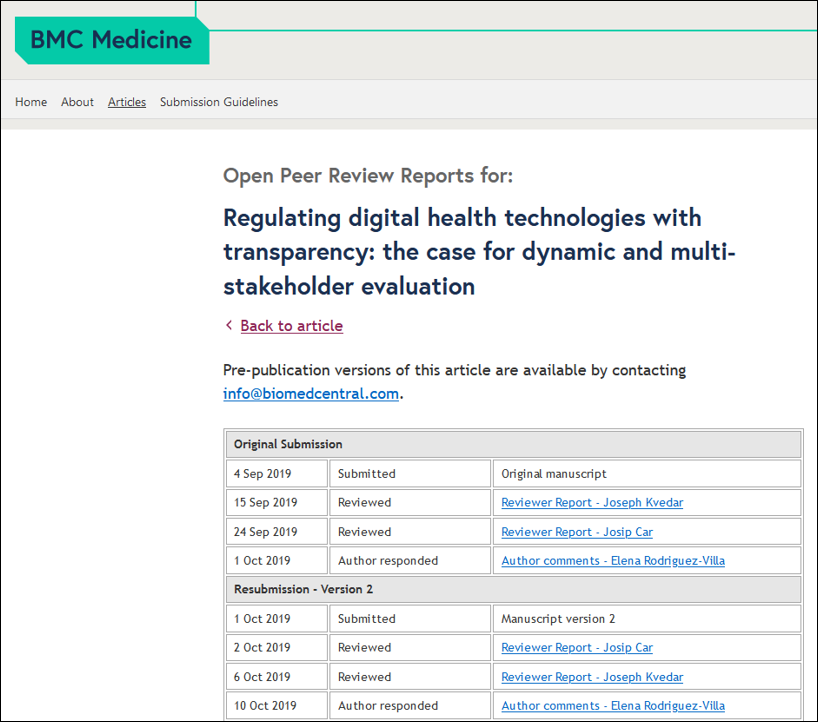
Since such open peer review is rarely employed by journals, we depend on information from secondary sources in this step. These sources may include platforms such as ResearchGate, Academia.edu, Retractionwatch.com and Retractiondatabase.org, where researchers share their experience with publishing. Naturally, the information obtained on these platforms needs to be assessed critically. For example, one cannot conclude that the journal as a whole or its publisher are untrustworthy after seeing one article with forged or otherwise manipulated results. Instead, one should check whether, for example, the editorial board of the journal properly retracted the article afterwards. Or in the case that one uses platforms such as ResearchGate, one must pay attention to whether the discussants support their claims with evidence.
Indexation of a journal in Journal Citation Reports (JCR) and Scopus may also indicate how reliable the journal is. This is because if a journal fails to meet JCR’s and Scopus’s evaluation criteria or exhibits non-standard citation practices, the journal is excluded from their interface accessible to users. Therefore, users should be interested in the reasons why the indexation of a journal was interrupted or terminated. JCR provides these reasons in a brief form in its title suppression list and Scopus in its discontinued titles list. If necessary, one can try to reconstruct their evaluation approach. When evaluating a journal indexed in JCR, one needs to focus on possible non-standard citation practices of the journal (a significant increase or fall in the number of citations, self-citations, and articles, majority of citations from a small group of journals) as well as on compliance with 28 criteria from JCR. In a journal indexed in Scopus, the following data are checked within the journal’s field: the self-citation rate, the total citation rate, CiteScore citation metrics, number of articles, number of full-text clicks and abstract usage.
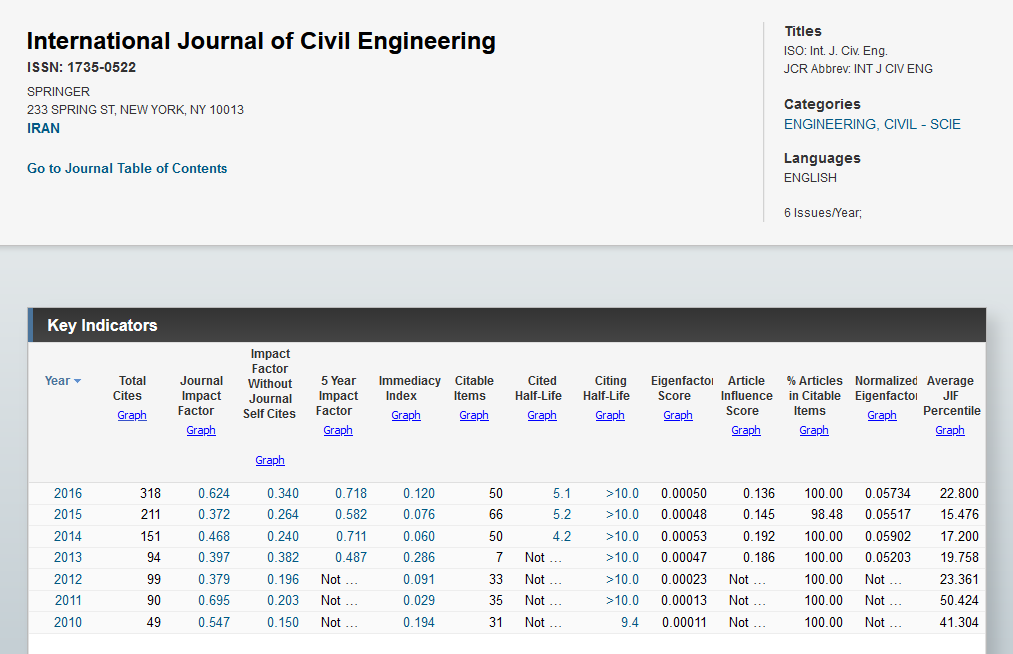
For example, in JCR’s title suppression list from 2019, the International Journal of Civic Engineering is listed with the note “Self”, which indicates that the value of its impact factor is influenced by a high number of self-citations.
If you look at the specific data about this journal in JCR, you will learn that while its impact factor value ranges from 0.372 to 0.695 (average 0.497), its impact factor value without self-citation varies between 0.150 and 0.382 (with an average of 0.254). With regard to the method of calculating the impact factor, this means that approximately half of the citations of articles published in the International Journal of Civil Engineering were self-citations. The administrators of JCR considered such a high number of self-citations too significant an influence on the impact factor and therefore excluded the journal from their list.
On the other hand, Scopus has the criterion “Number of articles”. Here it checks whether a journal published half the number of articles or less than other journals from the same field. However, it does not provide reasons for why the bar was set to half and not a different percentage. Moreover, this criterion ignores the fact that due to the varying publication schedules of journals, the number of articles published may differ as well.